Smart Beta ETFs are often known as ‘Strategic Beta‘ or ‘factor-based‘ ETFs. True to their name, these ETFs smartly choose their underlying assets. These ETFs pick the primary assets based on factors other than market capitalization.
ETFs generally classify their investment strategies as active or passive.
However, each had its pros and cons
So, avid thinkers and financial market gurus came up with a new approach that combines these strategies.


Most of the benchmarks today are constructed based on the market capitalization of the companies. The Market Capitalization of a company is the product of the share’s market price and the number of shares.
The use of market capitalization resulted in the neglect of other vital factors which could better judge the overall health and performance of the company.
For the S&P500 index, we can see that the weights assigned are:

As evident from the above tree map, the S&P500 is heavily skewed towards Apple, Microsoft, and Amazon-leading to passive ETFs being heavily tilted towards large-cap companies, reducing their potential returns.
Smart Beta represents a new way to build the underlying index. Smart beta is an index design process that aims to achieve superior risk-adjusted returns than traditional market capitalization-weighted benchmark indices.
The fund’s composition is set by various rules that exist whilst establishing the fund. These ETFs choose company stocks based on volatility expectations, dividend growth, total earnings, etc.
Smart Beta ETFs strategies
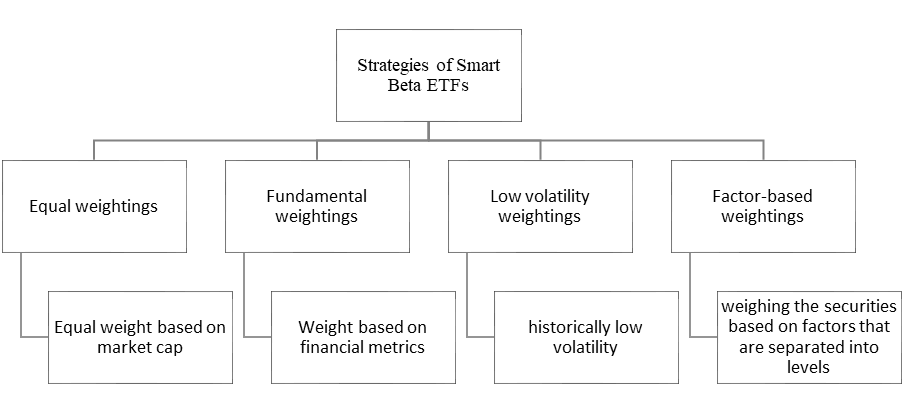
1. Equal weightings
Equal weight is assigned to the securities present in the index irrespective of the market capitalization of the firms.
For example, the Invesco S&P 500 Equal-Weight ETF (RSP) offers equal weights to the securities in the S&P500, unlike the index itself.
2. Fundamental weightings
Fundamental weighting is done based on various company fundamentals. Fundamentals such as profit, total revenue, cash flow, etc., are used.
The Invesco FTSE RAFI U.S. 1000 ETF is one fund linked to the FTSE RAFI Index. The index uses reported financial metrics of the companies to weigh them.
Metrics like cash flow, book value, total sales, and gross dividend consider the companies.
3. Low volatility weightings
The weightings in such ETFs are by using the historical volatility of the stocks – higher volatility implies higher risk.
The iShares MSCI EAFE Min Vol Factor ETF is based on less volatile stocks.
4. Factor-based weightings
The technique entails weighing securities according to factors divided into levels. Growing smaller enterprises, underpriced valuations, and balance sheet components are examples of such variables.
Some examples of factor ETFs are iShares MSCI USA Size Factor ETF (SIZE), iShares MSCI USA Momentum Factor ETF (MTUM), and iShares MSCI USA Value Factor ETF (VLUE) – depending upon factors like size, momentum, and value, respectively. We delve into the details of these factors later.
Advantages and Disadvantages of ETFs
Advantages of Smart Beta ETFs
- Increase returns, reduce risk, and maximize dividends. Smart beta ETF methods aim to reduce market volatility exposure while outperforming standard ETFs.
- Offer a plethora of strategies to choose from to diversify their portfolio.
- Smart Beta ETFs are strategy-oriented; an investor can find a suitable ETF that is in sync with the investor’s approach.
- Smart Beta ETFs have a higher expense ratio than passive ETFs but are still lower than actively managed ETFs.
Disadvantages of Smart Beta ETFs
- Since this is a comparatively newer method, the volume of these ETFs on the market might be lower, thus causing liquidity constraints.
- Although the expense ratio of a smart beta ETF may be lower than those charged by actively managed funds, the savings may not be noteworthy.
- Investors must consider several factors. As a result, the price of a smart beta ETF may differ from the fund’s underlying index value.
- Market-cap-weighted ETFs may beat smart beta ETFs in some market conditions.
If you want to invest in a strategy that incorporates active and passive investing, you should look at smart beta approaches.
FAQs
What are the advantages of smart beta ETFs?
Here are the advantages of smart beta ETFs:
Increase returns, reduce risk, and maximize dividends. Smart beta ETF methods aim to reduce market volatility exposure while outperforming standard ETFs.
Offer a plethora of strategies to choose from to diversify their portfolio.
Smart Beta ETFs are strategy-oriented; an investor can find a suitable ETF that is in sync with the investor’s approach.
Smart Beta ETFs have a higher expense ratio than passive ETFs but is still lower than actively managed ETFs.
What is a Smart Beta ETF?
Smart Beta represents a new way to build the underlying index. Smart beta is an index design process that aims to achieve superior risk-adjusted returns than traditional market capitalization-weighted benchmark indices.
The fund’s composition is set by various rules that exist whilst establishing the fund. These ETFs choose company stocks based on volatility expectations, dividend growth, total earnings, etc.
What disadvantages of smart Beta ETFs?
Since this is a comparatively newer method, the volume of these ETFs on the market might be lower, thus causing liquidity constraints.
Although the expense ratio of a smart beta ETF may be lower than those charged by actively managed funds, the savings may not be noteworthy.
The price of a smart beta ETF may differ from the fund’s underlying index value.
Market-cap-weighted ETFs may beat smart beta ETFs in some market conditions.
Reading the fund’s prospectus thoroughly is very important to understand all risks.